Geo-engineering is the study and implementation of technical ways to change (and arguably improve) things like weather patterns, river paths, soils, climates and sea currents on Earth. Recently, geo-engineering has received special attention for efforts to combat global warming.
Tuesday, November 4, 2008
Adding lime to seawater
Due to increased CO2 levels, the oceans have become more acid. Adding lime (calcium hydroxide) to seawater will increase the alkalinity of the water, making the water absorb more CO2 and reducing the release of CO2 from the water into the atmosphere.
Tim Kruger, a management consultant at London-based Corven, believes that this can be done most economically where there's plenty of limestone, and plenty of energy that is too remote to exploit for conventional commercial purposes.
"There are many such places — for example, Australia's Nullarbor Plain would be a prime location for this process, as it has 10,000km3 of limestone and soaks up roughly 20MJ/m2 of solar irradiation every day," said Kruger.
Although the process generates CO2 emissions, on paper it sequesters twice as much of the warming gas than it produces. Kruger says the process is therefore 'carbon negative'.
'This process has the potential to reverse the accumulation of CO2 in the atmosphere. It would be possible to reduce CO2 to pre-industrial levels,' he explained.
"We think it's a promising idea," says Shell's Gilles Bertherin, a coordinator on the project, which is being developed in an "open source" manner. "There are potentially huge environmental benefits from addressing climate change — and adding calcium hydroxide to seawater will also mitigate the effects of ocean acidification, so it should have a positive impact on the marine environment."
Sources and Links:
Shell Oil funds "open source" geoengineering project to fight global warming, at:
Mongabay.com
'Turning back the clock on climate change' - A technology to reverse climate change? To reduce ocean acidification? And that also promises to increase food production? Cath O’Driscoll investigates, at:
Chemistry & Industry Magazine
Adding lime to seawater feasibility study, funded by Shell, at:
Inventory of geo-engineering proposals
Thursday, October 23, 2008
Removing carbon from air - Discovery Channel
 Professor David Keith of the University of Calgary is working on a device that removes carbon dioxide directly from ambient air.
Professor David Keith of the University of Calgary is working on a device that removes carbon dioxide directly from ambient air.Keith has built a tower, 4 feet wide and 20 feet tall, with a fan at the bottom that sucks air in. Keith expects the air coming out at the top to have approximately 50% less carbon dioxide than the air coming in.
The tower features in an episode of Discovery Channel’s new “Project Earth” series on TV. The series has the largest budget of any in Discovery Channel’s history, and it may eventually attract a global viewership of more than 100 million.
The episode on Keith’s research has already aired in the U.S. - if you're missed it, you can watch it on Discovery Channel’s website, at: http://dsc.discovery.com/tv/project-earth/project-earth.html - click on “Episodes.”
If the program hasn't aired in your country, you may not get access to the online episode, but you can read more at: http://dsc.discovery.com/tv/project-earth/lab-books/fixing-carbon/guide1.html - also click on the links under "MORE CARBON".
The picture below describes the Big Picture of recycling, in which I envisage aviation to fund CO2 air capture. When talking about recycling, most people think about recycling of industrial products only. They may also see composting of organic waste as a (second) way of recycling. Instead of composting, I actually envisage organic waste to be burned by means of pyrolysis, in order to produce agrichar and hydrogen. I also envisage a third way of recycling that includes removing CO2 from the air. This CO2 could also be used for the production of agrichar and for commercial purposes such as to enrich greenhouses and for the production of building material, carbon fiber, etc. Furthermore, this CO2 could be used as fuel for aviation.
To tackle emissions by aviation, we can switch to airplanes and helicopters that are powered by batteries and hydrogen, or switch to fuels other than fossil fuel. Growth of algae could be assisted by such captured CO2, which could also be turned directly into fuel.
By financially supporting air capture of CO2 and the use of such CO2 to produce fuel, aviation could close the circle of this third way of recycling. This could make aviation environmentally sustainable. Since government is such a large user of aviation (both the military and civil parts of government), it makes sense for the government to start funding such air capture as soon as possible. An international agreement, to be reached in Copenhagen in 2009, could further arrange for the proceeds of environmental fees on commercial flights to fund such air capture and its use for fuel.

Further links:
http://dsc.discovery.com/tv/project-earth/explores/carbon.html - Discovery Channel
http://www.ucalgary.ca/news/september2008/keith-carboncapture - David Keith
http://www.ucalgary.ca/~keith/AirCapture.html - David Keith
http://www.ucalgary.ca/~keith/Misc/AC%20talk%20MIT%20Sept%202008.pdf - M.I.T.
views.blogspot.com - by Sam Carana
The post below is added for archival purposes. It was originally posted by Sam Carana at knol in 2009, which has meanwhile been discontinued by Google. The post received 4513 views at knol.
Funding of Carbon Air Capture
HOW CAN CO2 CAPTURE FROM AMBIENT AIR BEST BE FUNDED?
FEES ON JET FUEL CAN HELP FUND THE DEVELOPMENT OF CARBON CAPTURE FROM AMBIENT AIR.
 AIR CAPTURE of CO2 (carbon dioxide) is an essential part of the blueprint to reduce carbon dioxide to acceptable levels. Fees on
AIR CAPTURE of CO2 (carbon dioxide) is an essential part of the blueprint to reduce carbon dioxide to acceptable levels. Fees on  conventional jet fuel seems the most appropriate way to raise funding to help with the development of air capture technology.
conventional jet fuel seems the most appropriate way to raise funding to help with the development of air capture technology.Why target jet fuel? In most other industries, there are ready alternatives to the use of fossil fuel. Electricity can be produced by wind turbines or by solar or geothermal facilities with little or no emissions of greenhouse gases. In the case of aviation, though, the best we can aim for, in the near future at least, is biofuel or synthetic fuel, produced from CO2 captured from ambient air. As discussed below, development of these two forms of renewable energy can go hand in hand.
Additionally, the aviation industry can offset emissions, e.g. by funding air capture of carbon dioxide. The carbon dioxide thus captured could be partly used to produce fuel, which could in turn be used by the aviation industry, as pictured on the top right image. The carbon dioxide could also be used to assist growth of biofuel, e.g. in greenhouses and in algae bags, as described below.
 Algae can grow 20 to 30 times faster than food crops. As the CNN video on the right mentions, Vertigro claims to be able to grow 100,000 gallons of algae oil per acre per year by growing algae in clear plastic bags suspended vertically in a greenhouse. Given the right temperature and sufficient supply of light, water and nutrients, algae seem able to supply an almost limitless amount of biofuel.
Algae can grow 20 to 30 times faster than food crops. As the CNN video on the right mentions, Vertigro claims to be able to grow 100,000 gallons of algae oil per acre per year by growing algae in clear plastic bags suspended vertically in a greenhouse. Given the right temperature and sufficient supply of light, water and nutrients, algae seem able to supply an almost limitless amount of biofuel. Apart from growing algae in greenhouses, we should also consider growing them in bags. NASA scientists are proposing algae bags as a way to produce renewable energy that does not compete with agriculture for land or fresh water. It uses algae to produce biofuel from sewage, using nutrients from waste water that would otherwise be dumped and contribute to pollution and dead zones in the sea.
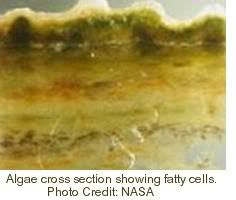
Apart from growing algae in greenhouses, we should also consider growing them in bags. NASA scientists are proposing algae bags as a way to produce renewable energy that does not compete with agriculture for land or fresh water. It uses algae to produce biofuel from sewage, using nutrients from waste water that would otherwise be dumped and contribute to pollution and dead zones in the sea.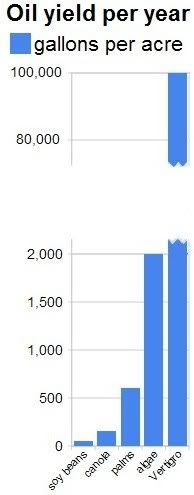 The NASA article conservatively mentions that some types of algae can produce over 2,000 gallons of oil per acre per year. In fact, most of the oil we are now getting out of the ground comes from algae that lived millions of years ago. Algae still are the best source of oil we know.
The NASA article conservatively mentions that some types of algae can produce over 2,000 gallons of oil per acre per year. In fact, most of the oil we are now getting out of the ground comes from algae that lived millions of years ago. Algae still are the best source of oil we know.In the NASA proposal, there's no need for land, water, fertilizers and other nutrients. As the NASA article describes, the bags are made of inexpensive plastic. The infrastructure to pump sewage to the sea is already in place. Economically, the proposal looks sound, even before taking into account environmental benefits.
Jonathan Trent, lead research scientist on the Spaceship Earth project at NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California, envisages large plastic bags floating on the ocean. The bags are filled with sewage on which the algae feed. The transparent bags collect sunlight that is used by the algae to produce oxygen by means of photosynthesis. The ocean water helps maintain the temperature inside the bags at acceptable levels, while the ocean's waves also keep the system mixed and active.
 The bags will be made of “forward-osmosis membranes”, i.e. semi-permeable membranes that allow fresh water to flow out into the ocean, while preventing salt from entering and diluting the fresh water inside the bag. Making the water run one way will retain the algae and nutrients inside the bags. Through osmosis, the bags will also absorb carbon dioxide from the air, while releasing oxygen. NASA is testing these membranes for recycling dirty water on future long-duration space missions.
The bags will be made of “forward-osmosis membranes”, i.e. semi-permeable membranes that allow fresh water to flow out into the ocean, while preventing salt from entering and diluting the fresh water inside the bag. Making the water run one way will retain the algae and nutrients inside the bags. Through osmosis, the bags will also absorb carbon dioxide from the air, while releasing oxygen. NASA is testing these membranes for recycling dirty water on future long-duration space missions.As the sewage is processed, the algae grow rich, fatty cells that are loaded with oil. The oil can be harvested and used, e.g., to power airplanes.
 A 2007 Bloomberg report estimated that the Gulf of Mexico's Dead Zone would reach more than half the size of Maryland that year and stretch into waters off Texas. The Dead Zone endangers a $2.6 billion-a-year fishing industry. The number of shrimp fishermen licensed in Louisiana has declined 40% since 2001. Meanwhile, U.S. farmers in the 2007 spring planted the most acreage with corn since 1944, due to demand for ethanol. As the report further describes, the Dead Zone is fueled by nitrogen and other nutrients pouring into the Gulf of Mexico, and corn in particular contributes to this as it uses more nitrogen-based fertilizer than crops such as soybeans.
A 2007 Bloomberg report estimated that the Gulf of Mexico's Dead Zone would reach more than half the size of Maryland that year and stretch into waters off Texas. The Dead Zone endangers a $2.6 billion-a-year fishing industry. The number of shrimp fishermen licensed in Louisiana has declined 40% since 2001. Meanwhile, U.S. farmers in the 2007 spring planted the most acreage with corn since 1944, due to demand for ethanol. As the report further describes, the Dead Zone is fueled by nitrogen and other nutrients pouring into the Gulf of Mexico, and corn in particular contributes to this as it uses more nitrogen-based fertilizer than crops such as soybeans. Professor David Keith (left) of the University of Calgary is working on a tower, 4 feet wide and 20 feet tall, with a fan at the bottom that sucks air in. The tower looks like it's made mainly of plastic, which could be made with carbon produced by such a tower. Inside the tower, limestone or a similar agent is used to bind the CO2 and to split CO2 off by heating it up. The limestone is recycled within the tower, although it does need to be resupplied at some stage. Anyway, the main cost appears to be the electricity to run it. Keith and his team showed they could capture CO2 directly from the air with less than 100 kilowatt-hours of electricity per ton of CO2. At $0.10/kWh, that would put the electricity cost at $10 per ton.
Professor David Keith (left) of the University of Calgary is working on a tower, 4 feet wide and 20 feet tall, with a fan at the bottom that sucks air in. The tower looks like it's made mainly of plastic, which could be made with carbon produced by such a tower. Inside the tower, limestone or a similar agent is used to bind the CO2 and to split CO2 off by heating it up. The limestone is recycled within the tower, although it does need to be resupplied at some stage. Anyway, the main cost appears to be the electricity to run it. Keith and his team showed they could capture CO2 directly from the air with less than 100 kilowatt-hours of electricity per ton of CO2. At $0.10/kWh, that would put the electricity cost at $10 per ton.
Jul 19, 2010
There are several efforts under development to produce a carbon-neutral fuel. Two of them were recently described in article in New Scientist, entitled: Green machine: Cars could run on sunlight and CO2.
http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn18993-green-machine-cars-could-run-on-sunlight-and-co2.html
See also Sandia
https://share.sandia.gov/news/resources/releases/2007/sunshine.html
Whereas many may think that this is a good way to power cars, I agree with you that it makes more sense to have electric cars. However, aviation is a bit more difficult to clean up, that's why aviation in particular can benefit from such technology, and that would justify that aviation made financial contributions to fund such developments.
As air capture technology matures with financial assistance funded by fees on aviation, it will be in a better position to develop into a more general technology used to reduce CO2 in the atmosphere to more acceptable levels.
http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn19308-the-next-best-thing-to-oil.html
http://www.sciencemag.org/content/330/6012/1797
Milking algae
Instead of harvesting algae for processing into biofuel, there is prospect for "milking" the algae, i.e. extracting oil from the algae without killing them.
This method is followed by Joule Unlimited.
http://www.theglobeandmail.com/news/opinions/opinion/a-brave-new-world-of-fossil-fuels-on-demand/article1871149/
And also by Algenol, Synthetic Genomics (Craig Venter’s venture) and BioCee
http://theenergycollective.com/tyhamilton/50300/joule-cool-not-alone-quest-sunlight-fuel-game-changer
Jul 5, 2011
British company set to make renewable jetfuel
British company Air Fuel Synthesis plans to capture carbon dioxide from the air, and mix it with hydrogen extracted from water through electrolysis, in order to make liquid hydrocarbon fuels for transport, including for aviation.
http://www.airfuelsynthesis.com/technology.html
http://www.airfuelsynthesis.com/technology/technical-review.html
http://www.airfuelsynthesis.com/faqs.html
Tuesday, January 15, 2008
Saturday, January 5, 2008
Scientists split CO2 into CO and hydrogen
The solar reactor contains 14 cobalt ferrite rings, each about one foot in diameter and turning at one revolution per minute. As an 88-square meter solar furnace blast sunlight into the unit, the rings heat up to about 2,600 degrees Fahrenheit. At that temperature, cobalt ferrite releases oxygen. The rings subsequently cool to about 2,000 degrees and are exposed to CO2. The cobalt ferrite, which is now missing oxygen, will take oxygen from the CO2. So, the reactor divides carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide and oxygen, leaving behind just carbon monoxide. With the cobalt ferrite restored to its original state, the reactor is ready for another cycle.
That carbon monoxide can then be used to make methanol or gasoline, which are essentially just combinations of hydrogen and carbon.
Scientists Use Sunlight to Make Fuel From CO2
http://www.wired.com/science/discoveries/news/2008/01/S2P
Cheers!
Sam Carana
Friday, November 30, 2007
Venus' runaway greenhouse effect a warning for Earth
Venus today is a hellish place with surface temperatures of over 400°C (752°Fahrenheit), winds blowing at speeds of over 100 m/s (224 mph) and pressure a hundred times that on Earth, a pressure equivalent, on Earth, to being one km (0.62 miles) under the sea.
Thursday, October 25, 2007
Combat Global Warming with Evaporative Cooling
Combat Global Warming with Evaporative Cooling - by Sam Carana
To combat global warming, wind turbines along the coastline could be used for the dual purposes of generating electricity at times when there is wind and evaporating water at times when there is no wind. Just a small breeze over the water can give the top water molecules enough kinetic energy to overcome their mutual attraction, resulting in evaporation of water and associated cooling of both water and air.
Such dual use of wind turbines can be implemented at many places where turbines overlook water; evaporation will work most effectively in hot and dry areas, such as where deserts or dry areas meet the sea or lakes. Evaporative cooling will add humidity to the air, which can also cause some extra rain and thus increase fertility of such dry areas as a beneficial side effect.
The energy needed to run the turbines can be obtained and stored in a number of clean, safe and renewable ways. ]
At times when there is plenty of wind, surplus energy from the turbines could be used to convert Water into hydrogen by means of electrolysis. Alternatively, bio-waste could be burned by means of pyrolysis to create both hydrogen and agrichar, which could be used to enrich soils. The hydrogen could be kept stored either in either compressed or liquid form, ready to power fuel cells that can drive the turbines at any time, day or night.
Another alternative is to run the turbines on electricity from concentrated solar thermal power plants in the desert. A desert area of 254 km² would theoretically suffice to meet the entire 2004 global demand for electricity. Ausra offers a solar thermal technology that uses the sun's heat to generate steam, which can then be stored for up to 20 hours, thus providing electricity on demand, day and night. Ausra points out that just 92 square miles of solar thermal power facilities could provide enough electricity to satisfy all current US demand.
Finally, there are some environmental concerns about wind turbines. There are concerns about carbon dioxide being released into the atmosphere in the process of making the concrete for the turbines. To overcome this, turbines could be made using alternative manufacturing processes, which can be carbon-negative. Furthermore, a recently completed Danish study using infrared monitoring found that seabirds steer clear of offshore wind turbines and are remarkably adept at avoiding the rotors.
In conclusion, wind turbines have a tremendous potential. They can potentially generate 72 TW, or over fifteen times the world's current energy use and 40 times the world's current electricity use. Offshore and near-shore turbines can make seawater evaporate and thus cool the planet, at times when they are not used to generate electricity.
References:
Ausra
http://ausra.com/
Wind power - Wikipedia
Solar power and electric cars, a winning combination!
Agrichar
Alternative method of manufacturing concrete
Massive Offshore Wind Turbines Safe for Birds
Footnote: This article was written by Sam Carana; it can be freely copied and published elsewhere, as long as the autor's name is retained in the article.
Monday, October 15, 2007
The FeeBate policy: a combination of a fee that funds a rebate
- a fee of 10% on sales of new cars with internal combustion engines, with proceeds used to fund rebates for electric cars
- a fee of 10% on sales of gasoline, with proceeds used to fund rebates on purchases and installation of facilities that produce renewable energy
- a fee of 10% on sales of coal, with rebates given when electricity suppliers install facilities that produce electricity from renewable sources
- a fee of 10% on building and construction work using concrete that contributes to global warming, with proceeds used to fund rebates on buildings that used clean concrete
- a fee of 10% on sales of fertilizers, with rebates on sales of agrichar
- a fee of 10% on sales of meat, with rebates and vouchers for vegan-organic foo
Agrichar
 Most households only use one or at most two different rubbish bins, one for recyclables (paper & packaging) and one for general waste. It makes a lot of sense to add a third type of rubbish bin, for biowaste, i.e. kitchen waste, soil and garden waste.
Most households only use one or at most two different rubbish bins, one for recyclables (paper & packaging) and one for general waste. It makes a lot of sense to add a third type of rubbish bin, for biowaste, i.e. kitchen waste, soil and garden waste.Many people already compost such biowaste in the garden, but all too often such biowaste disappears along with the general waste in the rubbish bin. As displayed on the picture below, analysis in Waikato, New Zealand, shows that about half of household waste can consist of kitchen waste, soil and garden waste. Such waste ends up on rubbish tips, where the decomposing process leads to greenhouse gases, such as methane. And all too often, farmers burn crop residues on the land, resulting in huge emissions of greenhouse gases.
 All such biowaste could deliver affordable energy by using the slow burning process of pyrolysis to produce agrichar or bio-char, a form of charcoal that is totally black. Organic material, when burnt with air, will normally turn into white ash, while the carbon contained in the biowaste goes up into the air as carbon dioxide (CO2). In case of pyrolysis, by contrast, biowaste is heated up while starved of oxygen, resulting in this black form of charcoal.
All such biowaste could deliver affordable energy by using the slow burning process of pyrolysis to produce agrichar or bio-char, a form of charcoal that is totally black. Organic material, when burnt with air, will normally turn into white ash, while the carbon contained in the biowaste goes up into the air as carbon dioxide (CO2). In case of pyrolysis, by contrast, biowaste is heated up while starved of oxygen, resulting in this black form of charcoal.This agrichar was at first glance regarded as a useless byproduct when producing hydrogen from biowaste, but it is increasingly recognized for its qualities as a soil supplement. Agrichar makes the soil better retain water and nutrients for plants, thus reducing losses of nutrients and reducing the CO2 that goes out of the soil, while enhancing soil productivity and making it store more carbon.
When biowaste is normally added to soil, the carbon contained in crop residue, mulch and compost is likely to stay there for only two or three years. By contrast, the more stable carbon in agrichar can stay in the soil for hundreds of years. Adding agrichar just once could be equivalent to composting the same weight every year for decades.
Agrichar appears to be the best way to bury carbon in topsoil, resulting in soil restoration and improved agriculture. Agrichar has the potential to remove substantial amounts of CO2 from the atmosphere, as it both buries carbon in the soil and gets more CO2 out of the atmosphere through better growth of vegetation. Agrichar restores soils and increases fertility. It results in plants taking more CO2 out of the atmosphere, which ends up in the soil and in the vegetation. Agrichar feeds new life in the soil and increases respiration, leading to improvements in soil structure, specifically its capacity to retain water and nutrients. Agrichar makes the soil structure more porous, with lots of surface area for water and nutrients to hold onto, so that both water and nutrients are better retained in the soil.
In conclusion, recycling biowaste in the above way is an excellent method to produce hydrogen (e.g. for cars) and to bury carbon in the soil and improve production of food. Agrichar is now produced for soil enrichment at a growing number of places. The top photo shows agrichar in pellet form from Eprida. Australian-based BEST Energies has built a demonstration pyrolysis plant with a capacity to process 300 kilograms of biowaste per hour. It accepts biowaste such as dry green waste, wood waste, rice hulls, cow and poultry manure or paper mill waste. The plant cooks the biomass without oxygen, producing syngas, a flammable mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen. The agrichar thus produced retains about half the carbon of the original biowaste (the other half was burned in the process of producing the syngas).
Also important is to compare different farming practices. Carbon is important for holding the soil together. Farmers now typically plough the soil to plant the seeds and add fertilizers. This ploughing causes oxygen to mix with the carbon in the soil, resulting in oxidation, which releases CO2 into the atmosphere. Ploughing leads to a looser soil structure, prone to erosion under the destructive impact of heavy rains, flooding, thunderstorms, wind and animal traffic. Given the more extreme weather that can be expected due to global warming, we should reconsider practices such as ploughing.
Furthermore, the huge monocultures of modern farming have become dependent on fertilizers and pesticides. The separation of farming and urban areas has in part become necessary due to the practice of spraying chemicals and pesticides. Instead, we should consider growing more food on smaller-scale farms, in gardens and greenhouses within areas currently designated for urban usage. Vegan-organic farming can increase bio-diversity; by carefully selecting complementary vegetation to grow close together, diseases and pests can be minimized while the nutritional value, taste and other qualities of the food can be increased.
An issue of growing concern is nitrous oxide (N2O), which is 310 times more potent than CO2 as a greenhouse gas when released in the atmosphere. Much release of N2O is related to the practices of ploughing and adding fertilizers to the soil. Microbes subsequently convert the nitrogen in these fertilisers into N2O. A recent study led by Nobel prize-winning chemist Paul Crutzen indicates that the current ways of growing and burning biofuel actually raise rather than lower greenhouse gas emissions. The study concludes that growing some of the most commonly used biofuel crops (rapeseed biodiesel and corn bioethanol) releases twice the amount of N2O, compared to what the International Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) estimates for farming. The findings follow a recent OECD report that concluded that growing biofuel crops threatens to cause food shortages and damage biodiversity, with only limted benefits in terms of global warming.
All this is no trivial matter. Soils contain more carbon than all vegetation and the atmosphere combined. Therefore, soil is the obvious place to look at when trying to solve problems associated with global warming. By changing agricultural practices, we can add carbon to the soil and can minimize release of greenhouse gases.
References:
- Soils offer new hope as carbon sink
http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/research/updates/issues/may-2007/soils-offer-new-hope/
- Surprise: less oxygen could be just the trick
http://tinyurl.com/ywalt4
- What we throw away
http://www.waikato.govt.nz/enviroinfo/waste/whatwethrowaway.htm
- The Carbon Farmers
http://www.abc.net.au/science/features/soilcarbon/
- Living Soil
http://www.championtrees.org/topsoil/
- BEST Pyrolysis, Inc.
http://www.bestenergies.com/companies/bestpyrolysis.html
- Eprida, Inc.
http://eprida.com/hydro/
- Biofuels could boost global warming, finds studyhttp://www.rsc.org/chemistryworld/News/2007/September/21090701.asp
- Biofuels: is the cure worse than the disease?
http://tinyurl.com/yq9t8o
Companies producing agrichar:
- terra preta at bioenergylists.org
http://terrapreta.bioenergylists.org/company
Communities without Roads
 Communities without roads is an exciting concept that allows people to live within walking distances of colleages, customers, friends, medical and educational facilities, shops, restaurants, etc. The sedentary lifestyle of many people is a result of the way cities are currently designed. Instead, we should facilitate the opposite, i.e. people coming out of their houses, offices, and especially their cars, in order to meet other people, getting better food and becoming more healthy in the process.
Communities without roads is an exciting concept that allows people to live within walking distances of colleages, customers, friends, medical and educational facilities, shops, restaurants, etc. The sedentary lifestyle of many people is a result of the way cities are currently designed. Instead, we should facilitate the opposite, i.e. people coming out of their houses, offices, and especially their cars, in order to meet other people, getting better food and becoming more healthy in the process.The car has come to dominate the urban landscape, resulting in a metropolitan conglomeration of suburbs, stringed together along highways. Our most fertile land is now used for roads and cars, and the industries needed to support them. About half the urban area is for buildings, mainly three-bedroom homes on small blocks of land. The other half is used for roads, parks and grassland between roads. A large part of roads, buildings and gardens is also used to park cars.
Ever less fertile land is available food. Global warming forces us to rethink all this. As prices of oil skyrocket, more land is being dedicated to grow bio-fuel, resulting in less land available for food. Also, more extreme weather conditions can be expected, resulting in increasing crop loss.
We need more land to grow fruit and vegetables, in ways as was once the case in traditional gardens and on smaller farms. One place to find such land is by converting roads and office blocks into gardens. This doesn't mean a return to those ‘good-old-days’ of small towns and villages. Instead, we should consider an entirely new type of urban design: communities without roads. Technological progress is not the enemy here. Better security and communication systems can help get such communities off the ground. Electric vehicles can be instrumental in getting such communities off the ground.
What I propose are communities with footpaths and bike-paths instead of roads. Houses would be built close together, around a local center of shops and restaurants. In communities without roads, houses could be smaller, since there's no need to park cars in front or in garages. Building houses close together itself reduces travel distances between them. Pathways to a nearby center could suffice for further daily travel, leading to shops, markets, restaurants, lecture and meeting rooms.
In such a center, people would conveniently eat in restaurants, without traffic and parking hassle and noise - just a short stroll by foot or ride on a bike or in an electric scooter. Eating out means less shopping, since food makes up most of our shopping. It also saves a lot of time - no more shopping, cooking, dishwashing and cleaning, no rubbish to get rid of. Walking more would be good for our health as well.
Living closer together means people could see each other more often, both at home or at such a nearby restaurant. Why travel to an office or University, when you can work or follow courses online? Homeschooling has long proven to be much more effective than school. Why should people be institutionalized, kids packed away into school, the elderly people into ‘homes’ and the sick in hospitals? Instead, we should encourage families to stay together as much as possible and as long as possible in communities without roads.
This would result in huge savings on the current cost of cars, roads, office buildings, car parks, garages, gasoline stations, etc. How much time and money could we save by reducing our daily travel between home and work? And how many lives would be saved if we had less car-accidents? Because of the shared walls between them, townhouses save on the cost of heating in winter and cooling in summer.
To start it off, a University campus could be transformed into a community without roads, where people live and come to learn and work. Anyone who would like to nominate one?
